
Management of hypotension: crystalloid solutions with dobutamine and norepinephrine titration.Insertion of central venous catheter, pulmonary catheter and invasive measurement of arterial pressure.Sometimes necessary analgosedation/muscle relaxation with artificial pulmonary ventilation with immediate inclusion of PEEP (end-expiratory pressure up to 10 cmH 2 O (1.0 kPa)).Blood sampling for hemocoagulation examination and lung amylase examination (statim), order a deleucotized erythrocyte mass.In the case of an incipient clinical picture of DIC, we quickly provide a blood reserve. The treatment is also similar to thromboembolism, complete DIC therapy as soon as possible, hypotension therapy, prophylaxis of renal failure and convulsions. Prophylaxis and treatment įor prophylaxis, similar general principles are recommended as for thromboembolism (specific procedures are not known).
#Dic amniotic fluid embolism skin#
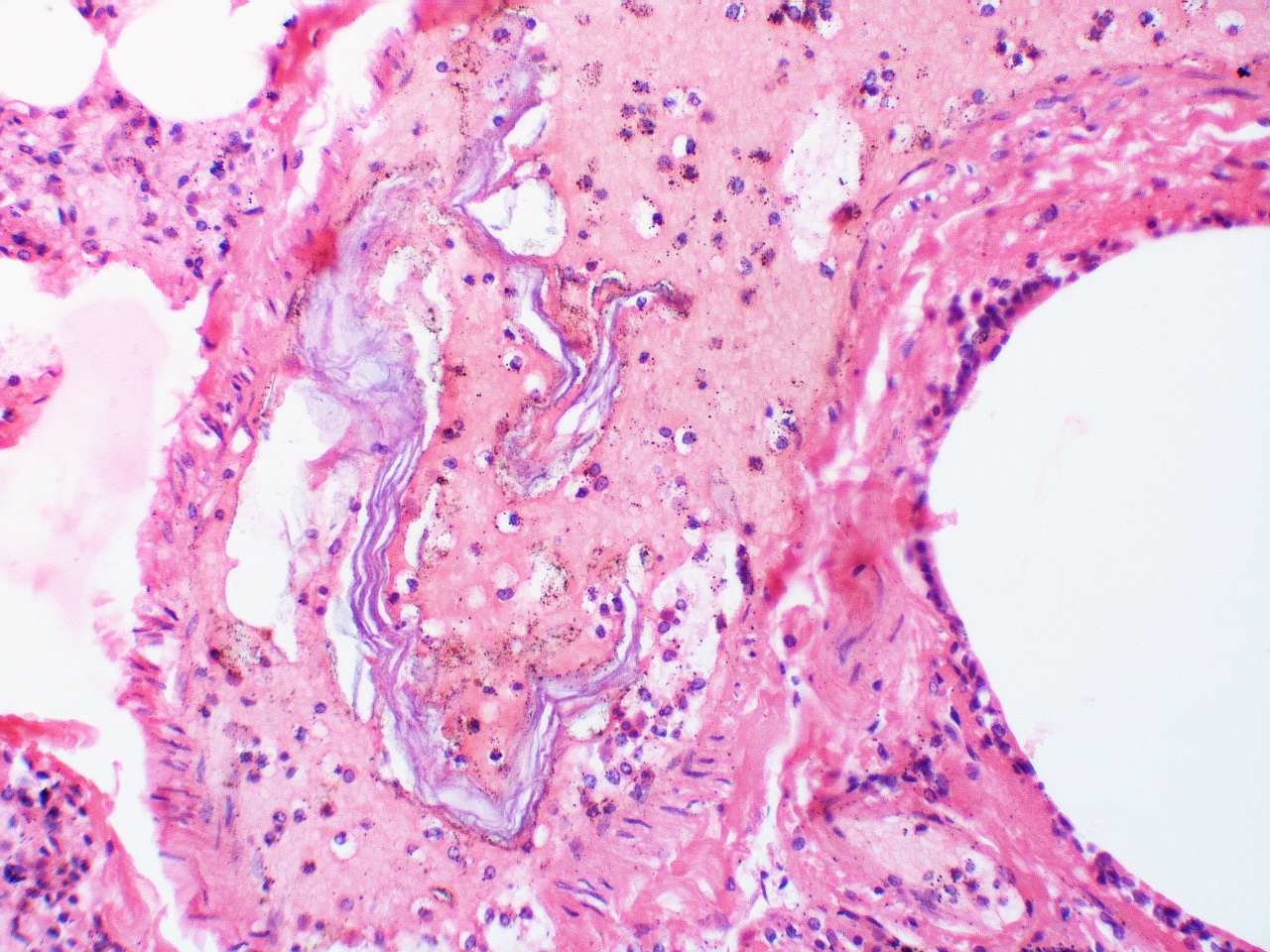
Based on the developing clinical picture, we try to terminate the pregnancy as quickly as possible.Īmniotic fluid embolism description Diagnosis ĭefinitively, amniotic fluid embolism is usually diagnosed post-mortem, based on findings in the lung tissue, where lanugo, fetal skin epithelium, and meconium bodies are typically found. Respiratory distress syndrome and acute renal failure develop, and the patient usually succumbs to this. If the patient survives, DIC symptoms develop within 15 minutes.

There is significant shortness of breath and hypotension with pO 2 falling below 80%. In the first stage, the symptoms of amniotic fluid embolism are the same as those of thromboembolism, namely cardiopulmonary failure in various ways. insertio velamentosa umbilicalis with a short umbilical cord (tear in the membranes).This condition requires immediate obstetric and anesthetic care.ĭifferent types of placental insertion – normal decidua, placenta accreta, placenta increta, placenta percreta The amniotic fluid enters the maternal circulation, where, similar to embolism of other etiology, shock develops. This is a very serious birth complication that occurs rarely (1:80,000 births). 3.2 Classification of DIC in obstetricsĪmniotic fluid embolism Īmniotic fluid embolism is the penetration of amniotic fluid into the mother's circulation with subsequent blocking of the pulmonary canal and the development of pulmonary hypertension.3 Disseminated intravascular coagulation.2.1 Obstetric causes of hypovolemic shock.

Her recent publications include The Health Factor, Coach Yourself To Better Health and Positive Thinking For Kids. As a former Midwife, Anne has a natural passion for writing about fertility, pregnancy, birthing and baby care. She has a special interest in integrating complementary medicine into conventional healthcare settings and is currently an Associate Tutor, lecturing in Health Coaching and Medical Hypnosis at Exeter University in the UK. Anne has also studied many forms of complementary medicine and has extensive experience in the field of clinical hypnosis. Her background includes working as a hospital midwife, Critical Care nurse, lecturer in Neonatal Intensive Care, and as a Clinical Nurse Specialist for a company making life support equipment. She is a former midwife and nurse teacher with over 25 years’ experience working in the fields of healthcare, stress management and medical hypnosis. Anne is a freelance lecturer and medical writer at Mind Body Ink.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
